Highly Selective HydrogenationThree-component catalysts, effective in the hydrogenation of simple ketones, are composed of Ruthenium(II) complexes with phosphine ligands(or diphosphine), 1,2-diamine, and a strong base. These catalysts were discovered by NOYORI Molecular Catalysis Project of Exploratory Research for Advanced Technology (ERAT) organized by Japan Science and Technology Corporation (JST). Subsequently, Exploration and Application Study (participants: Nagoya University, Aichi Institute of Technology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Takasago International Corporation, Nissan Chemical Ind., Ltd., Nippon Soda Co., Ltd., and Kanto Chemical Co., Inc.), supported by JST, improved the stability and ease of use of the Ruthenium(II) complexes through the development of a two-component catalyst.
These catalysts facilitate a highly efficient hydrogenation of simple ketones. In addition to high activity, the carbonyl-selective hydrogenation of aldehydes and ketones with conjugated or unconjugated carbon-carbon multiple bonds1) and the diastereoselective hydrogenation of various ketones2)3) is performed smoothly under mild conditions, such as at room temperature and/or under low hydrogen pressure(1 to 10 atom) resulting in corresponding alcohols in nearly quantitative yields. Chiral Ruthenium (II)-diphosphine complex, in combination with appropriate chiral diamine, catalyzes enantioselective hydrogenation of prochiral ketones to give chiral alcohols od a very high enantiomeric purity1)3),4). Furthermore, this catalyst is environmentally conscientious because of minimal metal disposal after the reaction, compared to the stoichiometric reduction with metal hydride reagents and the use of 2-propanol as a solvent5 Example of Hydrogenation Hydrogenation of unsaturated aldehydes and ketones1) Carbonyl compounds with conjugated or unconjugated carbon-carbon multiple bonds can be converted rapidly and quantitatively to the corresponding unsaturated alcohols. 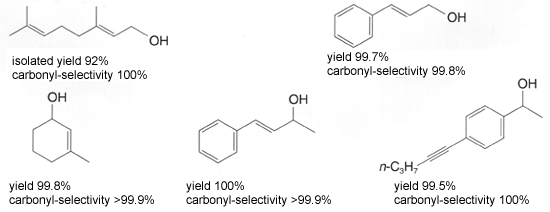 Diastereoselective hydrogenation of ketones2) 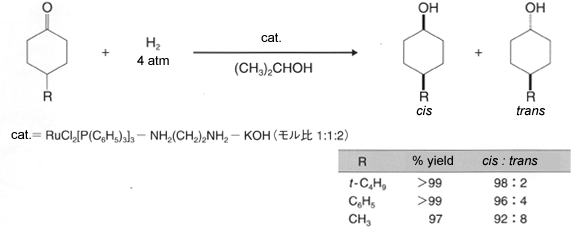 Enantioselective hydrogenation of ketones1)3),4) 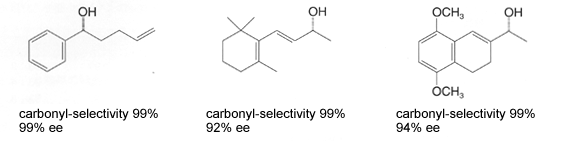
產品列表 | Item No | Product name | Packing | | 11400-65 | Dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine)(1,2-ethanediamine)ruthenium( II ) | 1g | | 11400-95 | | 200mg | | 11401-65 | Dichlorobis(tri-p-tolylphosphine)(1,2-ethanediamine)ruthenium( II ) | 1g | | 11401-95 | | 200mg | | 11404-65 | Dichloro[(R )-BINAP][(R,R )-DPEN]ruthenium( II ) | 1g | | 11405-65 | | 200mg | | 11405-95 | Dichloro[(R )-BINAP][(S,S )-DPEN]ruthenium( II ) | 1g | | 11402-65 | | 200mg | | 11402-95 | Dichloro[(S )-BINAP][(R,R )-DPEN]ruthenium( II ) | 1g | | 11403-65 | | 200mg | | 11403-95 | Dichloro[(S )-BINAP][(S,S )-DPEN]ruthenium( II ) | 1g | | 11408-65 | | 200mg | | 11408-95 | Dichloro[(R )-BINAP][(R )-DAIPEN]ruthenium( II ) | 1g | | 11409-65 | | 200mg | | 11409-56 | Dichloro[(S )-BINAP][(S )-DAIPEN]ruthenium( II ) | 1g | | 11409-95 | | 200mg |
參考文獻- T. Ohkuma, H. Ooka, T. Ikariya, and R. Noyori, Preferential Hydrogenation of Aldehydes and Ketones, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 117, 10417-10418 (1995)
- T. Ohkuma, H. Ooka, M. Yamakawa, T. Ikariya, and R. Noyori, Stereoselective Hydrogenation of Simple Ketones Catalyzed by Ruthenium( II ) Complexes, J. Org. Chem., 61, 4872-4873 (1996)
- T. Ohkuma, H. Ooka, S. Hashiguchi, T. Ikariya, and R. Noyori, Practical Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Aromatic Ketones, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 117, 2675-2676 (1995)
- T. Ohkuma, H. Ikehira, T. Ikariya, and R. Noyori, Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Cyclicα,β-Unsaturated Ketones to Chiral Allylic Alcohols, Synlett, 467-468 (1997)
- 大熊 毅,野依 良治,単純ケトン類の不斉水素化反応,有機合成化学協会誌,57,553-563(1996)
- H. Doucet, T. Ohkuma, K. Murata, T. Yokozawa, M. Kozawa, E. Katayama, A. F. England, T. Ikariya, and R. Noyori, trans-[RuCl2(phosphane)2(1,2-diamine)] and Chiral trans-[RuCl2(diphosphane) (1,2-diamine)]: Shelf-Stable Precatalysts for Rapid, Productive, and Stereoselective Hydrogenation of Ketones, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 37, 1703-1707 (1998)
產品介紹 |