不對稱還原觸媒Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation CatalystsAsymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation Catalysts were discovered by NOYORI Molecular Catalysis Project ( ERATO ).
Chiral Rethenium complexes with diamine ligands are very effective catalysts for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation reactions of ketones or imines, and give optically active alcohols or amines in high optical yields. Using 2-propanol or formic acid as hydrogen source, asymmetric transfer hydrogenation reaction is easily achieved in laboratory flask without special equipments. Asymmetric Hydrogenation Catalysts(Chloro complex)
RuCl[(S,S )-Tsdpen](η6-arene) | Asymmetric Hydrogenation Catalysts(Amide complex)
Ru[(S,S )-Tsdpen](η6-arene) | RuCl[(S,S )-Msdpen](η6-arene) | 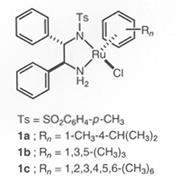 | 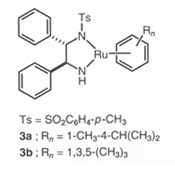 | 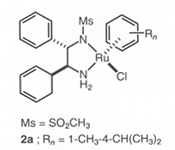 |
※RuCl(Tsdpen)(η 6-arene),Cp*RhCl(Tsdpen) and Cp*IrCl(Tsdpen)are available. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones 1)-11) (Synthesis of Optically active Secondary Alcohols) 《Selection of hydrogen source》 2-Propanol or formic acid can be used as hydrogen donor in this hydrogenation reaction. The hydrogenation reaction in 2-propanol solvent is reversible, so concentration of substrates and molar ratio of substrates /catalyst have to be optimized. On the other hand, the hydrogenation reaction using formic acid as hydrogen donor is irreversible and high optically pure chiral alcohol can be obtained in high yield even if under high concentration of substrates and high molar ratio of substrates / catalysts. Reaction using 2-Propanol as hydrogen source 1), 3), 5)-7), 9)Reaction using Formic acid as Hydrogen source 2), 3), 5)《Selection of substrates》 In addition to hydrogenation of simple ketones, these catalysts facilitate a high efficient hydrogenation of the undermentioned ketones with carbon-carbon multiple bonds or hetero atomic functional groups without damage to functional groups, and give chiral alcohols with a high optically purity. For example, 97% ee acetylene alcohol is obtained by hydrogenation of acetylene ketone and hydrogenation of ketones with furan or thiophene cyclic structure is performed smoothly and gives chiral alcohols with a high optically purity. And hydrogenation of pyridyl ketones is also performed smoothly and gives 95% ee optically active pyridyl alcohols. This hydrogenation is applied to ketones with polyfunctional groups, for example pyridyl, carbon-carbon double bonds or ester groups, and synthesis of key intermediates of carbonic anhydrase inhibitor or MK-0417 is achieved. Furthermore, in case of hydrogenation of unsymmetric 1,2-diketone, optically active α-hydroxyketone or optically active 1,2-diol compound can be produced selectively by control of reaction conditions. And more, hydrogenation of acetophenones with 2-cyano, 2-azido or 2-nitro group is performed effectively to give optically active alcohols, and they are reduced easily by common reductants and become optically active aminoalcohols for useful intermediates of medicines. Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Benzils 12) (Synthesis of Optically active Hydrobenzoins) Benzils are reduced rapidly and can be converted quantitatively to optically active hydrobenzoins with high optically purity in a mixed solvent of formic acid and triethylamine under mild conditions such as at room temperature by chiral Ruthenium catalyst. Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Secondary Alcohols 5), 13)Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation in 2-propanol solvent is reversible, so enantioselective hydrogenation with a high enantiomeric purity was difficult for high reduction potential ketones with electron donor group on aromatic ring. But, optically active alcohols can be obtained in high optical yields by kinetic resolution of racemic alcohols using chiral Ruthenium catalysts. This method applies to synthesis of (-)-chokol G and (-)-pentenomycin like natural substances. | unreacted alchol | | | substrate | catalyst | time, h | recovery, % | ee, % | config | kf/ks | 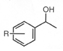 | | R = H | 3a | 36 | 50 | 92 | R | >80 | | R = p-OCH3 | 3a | 22 | 47 | 92 | R | >30 | | R = p-N(CH3)2 | 3b | 30 | 44 | 98 | R | >30 |  | | R = CH2 | 3a | 6 | 47 | 97 | R | >40 | | R = (CH2)2 | 3a | 6 | 49 | 99 | R | >50 |
S/C = 500 Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Imines 5), 16), 17)In the past, it was difficult to synthesize optically active amines from imines by asymmetric hydrogenation using catalysts. These catalysts facilitate a highly efficient hydrogenation of imines and give optically active amines in high optical yields.
參考文獻S. Hashiguchi, A. Fujii, J. Takehara, T. Ikariya, R. Noyori, “Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Aromatic Ketones Catalyzed by Chiral Ruthenium(II) Complexes”, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 117, 7562-7563 (1995) A. Fujii, S. Hashiguchi, N. Uematsu, T. Ikariya, R. Noyori, “Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed Asymmetric Transfer Hydro- genation of Ketones Using a Formic Acid-Triethylamine Mixture”, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 118, 2521-2522 (1996) 橋口昌平、藤井章雄、野依良治、“金?錯体触媒?用? ????????????類?水素移動型不?還元反?”、有機合成化?協?誌、54,818-828 (1996) K. Matsumura, S. Hashiguchi, T. Ikariya, R. Noyori, “Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of α,β-Acetylenic Ketones”, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 8738-8739 (1997) R. Noyori, S. Hashiguchi, “Asymmetric Transfer Hydro- genation Catalyzed by Chiral Ruthenium Complexes”, Acc. Chem. Res., 30, 97-102 (1997) K. OKano, K. Murata, T. Ikariya, “Stereoselective Synthesis of Optically active Pyridyl Alcohols via Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Pyridyl Ketons’’, Tetrahedron Lett., 41, 9277-9280 (2000) T. Koike, K.. Murata, T. Ikariya, “Stereoselective Synthesis of Optically Active α-Hydroxy Ketones and anti-1,2-Diols via Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Unsymmetrically Substituted 1,2-Diketones”, Org.. Lett.., 2, 3833-3836 (2000) M. Watanabe, K. Murata, T. Ikariya, to be published. M.J. Palmer, M. Wills, “Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of C=O and C=N Bonds”, Tetrahedron:Asymmetry, 10, 2045-2061 (1999) K.-J. Haack, S. Hashiguchi, A. Fujii, T. Ikariya, R. Noyori, “The Catalyst Precursor, Catalyst, and Intermediate in the RuII-Promoted Asymmetric HydrogenTransfer between Alcohols and Ketones”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 36, 285-288 (1997) M. Yamamoto, H. Ito, and R. Noyori, "The Metal-Ligand Bifunctional Catalysis. A Theoretical Study on the Ruthe- nium(II)-Catalyzed Hydrogen Transfer Between Alcohols and Carbonyl Compounds” , J. Am. Chem. Soc., 122, 1466-1478 (2000) K. Murata, K. Okano, M. Miyagi, H. Iwane, R. Noyori, T. Ikariya, “A Practical Stereoselective Synthesis of Chiral Hydro- benzoins via Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Benzils”, Org.Lett., 1, 1119-1121 (1999) S. Hashiguchi, A. Fujii, K.-J. Haack, K. Matsumura, T. Ikariya, R. Noyori, “Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Secondary Alchols by RuII-Catalyzed Hydrogen Transfer”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., , 36, 288-290 (1997) R.M. Kanada, T. Taniguchi, K. Ogasawara, “Asymmetric Hydrogenation Transfer Protocol for Enantiocontrolled Synthesis of (-)-Chokol G”, Chem. Commun., 1998, 1755. Y. Iura, T. Sugahara, K. Ogasawara, “Oxidative Resolution of 2-Cyclopentenols By the Asymmetric Hydrogenation Transfer Protocol ”, Tetrahedron Lett., 40, 5735-5738 (1999) N.Uematsu, A.Fujii, S.Hashiguchi, T.Ikariya, R.Noyori, “Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Imines”, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 118, 4916-4917 (1996) 橋口昌平、藤井章雄、野依良治、“???類?不?還元反?”、有機合成化?協?誌、55,413-423 (1997)
關連製品| Auxiliary Chiral Ligands | | 製品名 | 光學純度 | Cat.No | 包裝 | 價格 | | (1S, 2S )-N-(p-Toluenesulfonyl)-1,2-diphenylethanediamine (S,S )-TsDPEN | >99.0% ee(HPLC) | 41051-55 | 5g | inquiry | | 41051-65 | 1g | inquiry | | (1R, 2R )-N-(p-Toluenesulfonyl)-1,2-diphenylethanediamine (R,R )-TsDPEN | >99.0% ee(HPLC) | 41052-55 | 5g | inquiry | | 41052-65 | 1g | inquiry | | (1S, 2S )-N-(Methanesulfonyl)-1,2-diphenylethanediamine (S,S )-MsDPEN | >99.0% ee(HPLC) | 25954-55 | 5g | inquiry | | 25954-65 | 1g | inquiry | | (1R, 2R )-N- (Methanesulfonyl)-1,2-diphenylethanediamine (R,R )-MsDPEN | >99.0% ee(HPLC) | 25953-55 | 5g | inquiry | | 25956-65 | 1g | inquiry | | Auxiliary Ruthenium Complexes | | 製品名 | 純度 | Cat.No | 包裝 | 價格 | | Dichloro(p-cymene)ruthenium(Ⅱ), dimer [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 | >99 % | 11443-35 | 25g | inquiry | | 11443-55 | 5g | inquiry | | 11443-65 | 1g | inquiry | | | | Chiral Auxiliaries | | 製品名 | 光學純度 | Cat.No | 包裝 | 價格 | | (1S, 2S )-(-)-1,2-Diphenyl-1,2-ethanediamine | 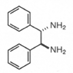 |
| >99.0% ee(HPLC) | 11445-35 | 25g | inquiry | | 11445-55 | 5g | inquiry | | 11445-65 | 1g | inquiry | | (1R, 2R )-(+)-1,2-Diphenyl-1,2-ethanediamine | 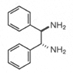 |
| >99.0% ee(HPLC) | 11444-35 | 25g | inquiry | | 11444-55 | 5g | inquiry | | 11444-65 | 1g | inquiry | | (S,S )-(-)-Hydrobenzoin | 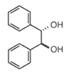 |
| >99.0% ee(HPLC) | 18618-35 | 25g | inquiry | | 18618-55 | 5g | inquiry | | (R,R )-(+)-Hydrobenzoin | 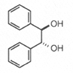 |
| >99.0% ee(HPLC) | 18617-35 | 25g | inquiry | | 18617-55 | 5g | inquiry | | Auxiliaries Ruthenium Salt | | 製品名 | 純度 | Cat.No | 包裝 | 價格 | | Ruthenium(Ⅲ) chloride n-hydrate RuCl3‧nH2O | >37 %(as Ru) | 36502-35 | 25g | inquiry | | 36502-55 | 5g | inquiry | | 36502-65 | 1g | inquiry |
|